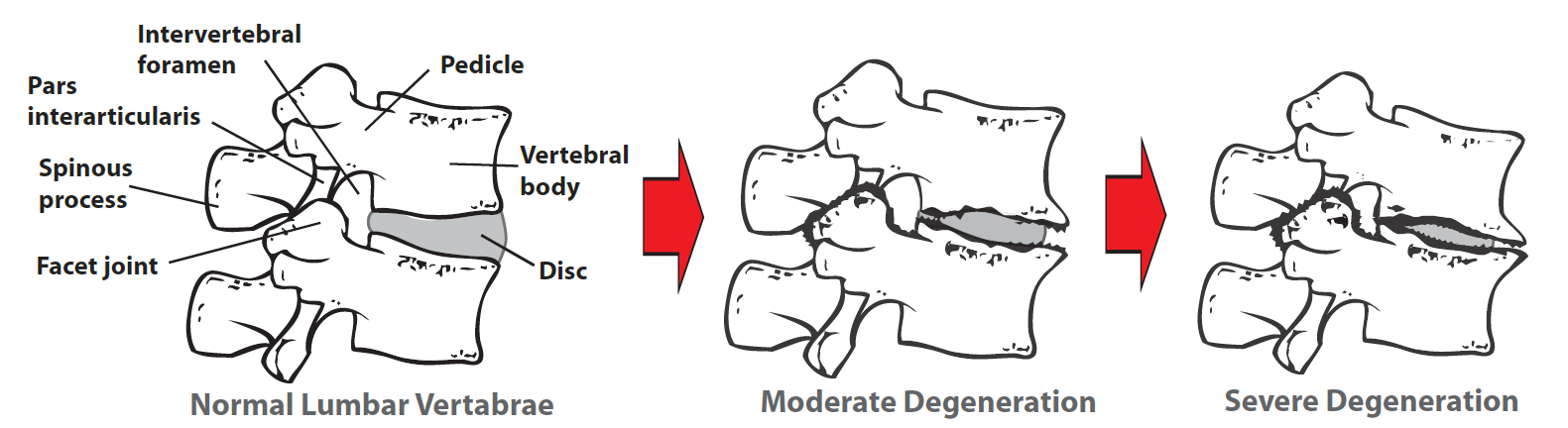
Overview - Osteoarthritis or Degenerative Joint Disease (DJD) is a progressive, noninflamatory disease characterized by changes to joint cartilage and related components. Typically, the large weight bearing joints are most affected such as the spine and knees. The exact mechanism is not well understood, however the sequence of changes are well documented.
Symptoms - Pain or aching, stiffness, decreased range of motion (or flexibility), swelling
Risk Factors
- Joint injury and overuse - repetative strain increases risk
- Gender - Women over 50 years are more likely to develop osteoarthritis than men
- Weight - Extra weight puts stress on the hips and knees
- Genetics - People with family members who have osteoarthritis are more likely to develop it themselves.
Treatment
- local muscle strengthening and general aerobic exercise
- heat/cold
- manipulation and stretching (particularly for osteoarthritis of the hip)
- interventions to achieve weight loss for those who are overweight or obese
- transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) for pain relief
- appropriate footwear with shock-absorbing properties
- assessment for orthotics/bracing/joint supports
- assistive devices (e.g., walking sticks and tap turners)

Head & Neck
Shoulder & Arm
Back
Hip & Leg
Ankle & Foot
